Many of us are used to back pain, which disrupts normal life for a long time. Although the cause may be trauma, neuropathy or spinal deformity, osteoporosis of the lumbar spine often becomes a trigger for discomfort. This degenerative disease can occur even at a young age, its initial manifestations can be detected even in adolescents and students, but the majority of patients are after 40 years of age. Changes in the spine associated with osteonecrosis can occur in any part, from the cervix to the lumbar to the lumbar and sacrum. But the most common form that gives people a lot of discomfort and pain is lumbar spine tumors. What is this disease, what disease manifest and the phenomenon of pain in the lower back always speaks for this disease.
Lumbar spinal cord tumors: what is the essence of the pathology?
Osteochondrosis is a term derived from two words: osteon in Greek, meaning bone and chondron, which is cartilage. Consequently, bone degeneration of the lumbar spine (and all other regions) is initiated by changes in the cartilage of the disc, which is the natural "lining" between the vertebrae and the internal shock absorber. movement. Changes in the structure of the disc and its function are accompanied by a natural response in the vertebral body. With this disease, gradual degenerative changes occur in the disc body. The height of the disc decreases, as a result of which its physiological function is lost, the instability and changes of the vertebral joints are caused. As the disease progresses, a reaction occurs at the end of the vertebral body. This reaction can be divided into three phases: malnutrition and dystrophic edema, fat degeneration and the terminal sclerosis.
Causes of osteonecrosis of the spine
Our vertebral discs begin to slowly deform and change when we are about 20 years old. A gradual decrease in fluid in the disc body leads to a decrease in the size of the space between the vertebrae (chondrosis). This means that the disc can no longer act as a shock absorber and the tension of the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments of the vertebra changes. As a result, much greater loads are imposed on the vertebral joints, increasing from year to year. The spinal ligaments are not properly positioned and stretched unevenly, the moving segments of the spine gradually become unstable. The dorsal segment usually consists of two adjacent vertebral bodies and a disc between them. The upper and lower head plates in the vertebral body are subjected to more pressure, thickening areas (sclerosis) and border burrs (vertebrae) gradually develop. Due to such changes, the full clinical picture of the disease is shaped in the future.
What are the symptoms of lumbar fibroids?
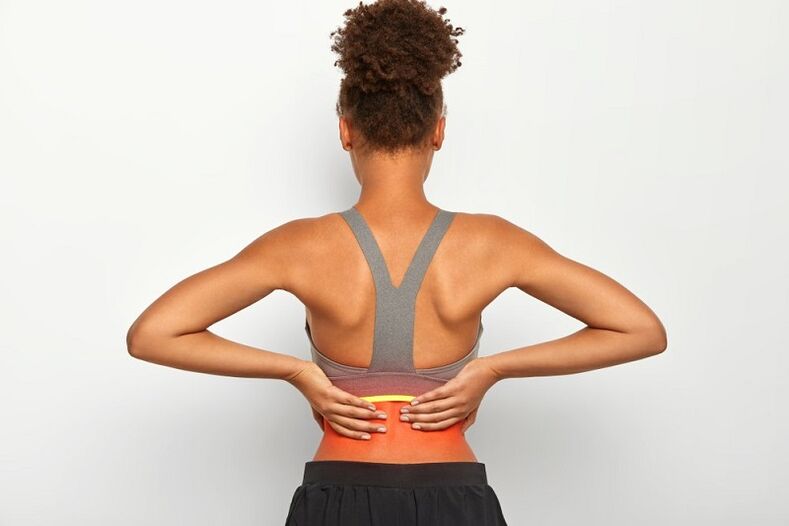
Almost all forms of the disease present themselves as severe back pain, difficult to control and affecting a specific segment of the spine (from the neck to the lower back and the sacrum). Symptoms of lumbar spondylolisthesis may be confined to the spine only (in the lumbar region) or to the legs if they originate from the lumbar spine, or the arm if they originate from the cervical spine. .
Symptoms can occur with rest, exertion, or routine activity. There may be lens compression, irritation in the nerve root region, or lens phony symptoms if the cause is in the facial joint or nearby muscles. Usually, lumbar spinal cord tumors combined with lesions in other areas - the chest, the cervical spine - the symptoms will be wider. In other words, discomfort and pain not only causes one segment to be damaged, but multiple areas of bone necrosis at the same time. The disease has an undulating course with episodes of severity (symptoms can severely affect normal life) and is in temporary remission, when symptoms subside or almost disappear. But any factor, physical or mental, can lead to a sudden relapse.
How is spinal cord tumors diagnosed?
The diagnosis is based on the study of the patient's medical history and complaints, physical examination with identification of typical symptoms, and neurological examination. Nowadays, there is a growing tendency for doctors to carry out diagnostic tools, since other pathologies are often hidden under the guise of osteonecrosis.
For example, among patients with persistent back pain and planning surgery for pain relief, bone health is a key factor. If a patient is found to have low bone density before surgery, this may affect the bone necrosis treatment plan before, during, and after the procedure. A study from the Special Surgery Hospital (HSS) in New York found that lumbar spine computed tomography before surgery revealed a significant number of patients with low bone density that had not previouslydiagnose.
Nearly half of the nearly 300 patients examined are diagnosed with osteoporosis, or its precursor, osteoporosis. It is especially important to take this into account at the age of over 50. The low bone mineral density ratio in this group is 44%, and 10, 3% is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Low bone density is a known risk factor for spinal fractures and the condition can be an aggravating factor in the treatment of osteonecrosis.
Treatment of spinal necrosis

Treatment options depend on the severity of your symptoms. Physiotherapy is the primary method of pain relief in the early stages. Ultrasound, electrotherapy, and heat treatment were used. Treatment is complemented by proper pain management such as NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and steroids. Practice injection can be used - blockade, trigger point injection. Shown are manual therapy, osteopathy, exercise therapy.
Surgical treatment is always the last resort. There are situations that need surgery. An example might be bladder or rectal paralysis due to spinal stenosis or disc prolapse, a large herniated disc. Options for the activity are selected together with the doctor. But after surgical treatment, the problem is not completely eliminated, a long-term rehabilitation and lifelong supportive treatment is required. This is due to the fact that bone necrosis does not go away anywhere, it can progress in other parts.













































